How can we monitor bandwidth consumption on Windows server?
Q: We need to know how much bandwidth consumes our Windows server. What is the easiest way to accomplish that?
A: IPHost Network Monitor, since version 3.5, offers WMI Traffic Volume monitor. The sequence of its setup is described below.
WMI Traffic Volume monitor description
Start New Monitor wizard and select WMI Traffic Volume monitor.
On the next screen select host name and, if necessary, check the checkbox to start monitor upon creation.
On the third screen set the monitor’s parameters. Note that we only will comment on monitor type-specific settings; all the rest are common settings for monitors, explained in online help.

Select network interface (if necessary) to measure traffic speed for. Click on ellipsis to the right of Interface Name value to see the whole list of interfaces reported by WMI:
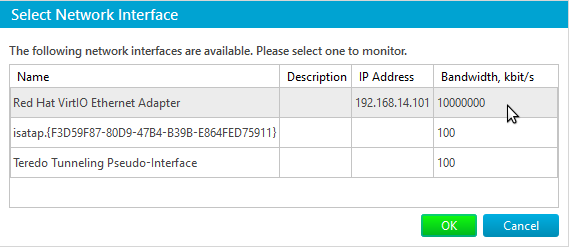
Most probably you will see several interfaces, but you only should be interested in those with assigned IP address. Run ‘ipconfig /all’ command in cmd.exe in separate window to choose appropriate interface.
Program will prefill Interface Bandwidth (network interface speed capacity). However, you can change that value if required. This value is used to normalize measured value, if percentage is selected (see below). Note: if set to zero, program will assume the value of 1.
Measure (traffic) drop-down allows you to measure total (incoming and outgoing) traffic volume (by default), incoming or outgoing only. Note: when Data Set is changed, the statistics calculated so far will be reset. You will be warned by a pop-up window if you choose to alter Data Set.
and show (traffic) as allows you to choose how to display the calculated traffic volume: in kilobytes, megabytes or gigabytes. Default is in megabytes.
Store traffic data for allows you to select the time interval to store collected traffic data for monitor being created:
Authentication credentials are used to access WMI services. Usually, those are credentials of an account with administrative rights.
You are given granularity in minutes, hours, days, weeks or months. Note that summation period means from what distance in the past is traffic volume measured. I.e., if 1 hour is set, then the traffic measured starts from exactly one hour ago till current moment.
WMI and SNMP monitoring
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is de facto standard protocol used to request information from network devices and/or control certain functions of those. In case of Windows you can use either WMI or SNMP traffic volume monitors. The choice is entirely up to you; if you have a heterogeneous network, SNMP method can be used for uniformity, since WMI is Windows-only means.
Note: you need to explicitly enable SNMP Services on Windows computer you need to monitor (via Add/Remove Windows Components). Don’t forget to right-click on the services to set up required parameters such as community names. Please refer to Net-SNMP documentation on the meaning of those settings.
The two methods to monitor traffic volume can return slightly different results, due to many a difference of measurement approaches.
Related Topics:
We need to monitor bandwidth consumption by T1 routers on our network, is it possible with IPHost Network Monitor?
How to measure bandwidth consumption on Linux server?

